مبدأ ارخميدس

To read the English version click here.
توضح هذه التجربة أنه عند وضع جسم ما في سائل، يزيح الجسم كمية من السائل تساوي كتلتها كتلة الجسم نفسه. علاوة على ذلك، فإن حجم السائل المُزاح يساوي حجم الجزء المغمور من الجسم.

To read the English version click here.
توضح هذه التجربة أنه عند وضع جسم ما في سائل، يزيح الجسم كمية من السائل تساوي كتلتها كتلة الجسم نفسه. علاوة على ذلك، فإن حجم السائل المُزاح يساوي حجم الجزء المغمور من الجسم.

توضح هذه التجربة أنه عند انعدام مقاومة الهواء، يصل جسمان يسقطان بحرية من نفس الارتفاع إلى الأرض في نفس اللحظة. يكتسب كلا الجسمين نفس السرعة أثناء السقوط، مما يثبت أنهما يختبران نفس التسارع – تسارع السقوط الحر. تشرح التجربة سبب رؤيتنا للأجسام الثقيلة تسقط أسرع من الأجسام الخفيفة بسبب تأثيرات مقاومة الهواء.
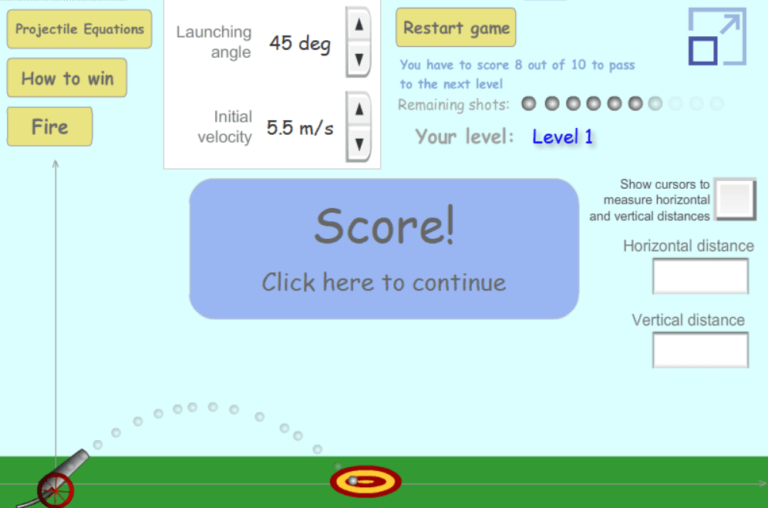
In this game, you must employ the projectile equations to win.
The game consists of three levels, each of which must be completed by scoring at least 8 out of a possible 10 tries. In the first level, you must hit a ground target that shifts position after each attempt. In the second level, you will need to alter the ball’s trajectory to pass over a wall. In the third level, the target flies and changes position both horizontally and vertically in each trial.
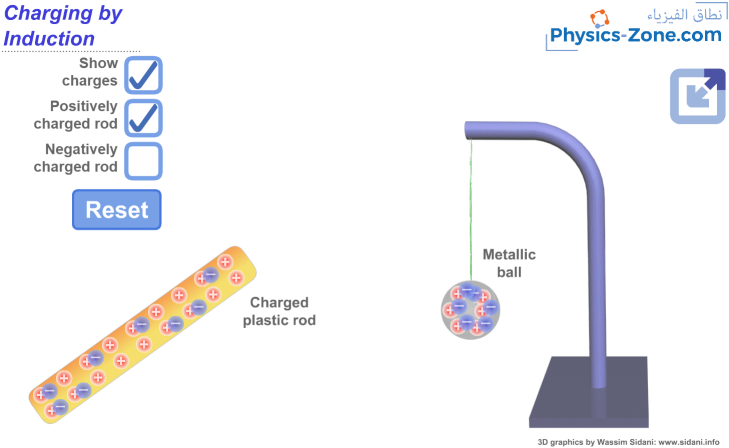
Using this simulation, you can experience the phenomenon of charging a metallic ball by induction in the first stage and charging the ball by contact in the second stage after the charged rod touches the ball. The displayed charges are for an illustrational purpose, and they are not seen in reality. You can disable the display of charges on the rod and on the ball.
In this simulation, you can try two situations, one in which the rod is positively charged and another in which the rod is negatively charged, and you will see that the two situations result in the same observation.

If you or your student or child are having difficulties in learning long division, then you will find this simulation comprehensive and instructional, that guides the learner through the process step by step. This application is for long division with float quotient. Another application on long division with remainder is also available in the simulations section.

This demonstration explains torque (moment of force) and rotational equilibrium. A force can create a turning effect that depends on both the force magnitude and the perpendicular distance from the pivot point. At equilibrium, clockwise moments equal counterclockwise moments. The post includes formulas for calculating torque with perpendicular and angled forces.
I created this course and published it on my Moodle platform. Each module is a SCORM package, with a course evaluation survey at the end and an unofficial completion certificate as a template that can be costumed to the specifications of your organization. The course is tracked, and you must successfully complete each chapter to unlock the next one. The course is fully learner-centered.