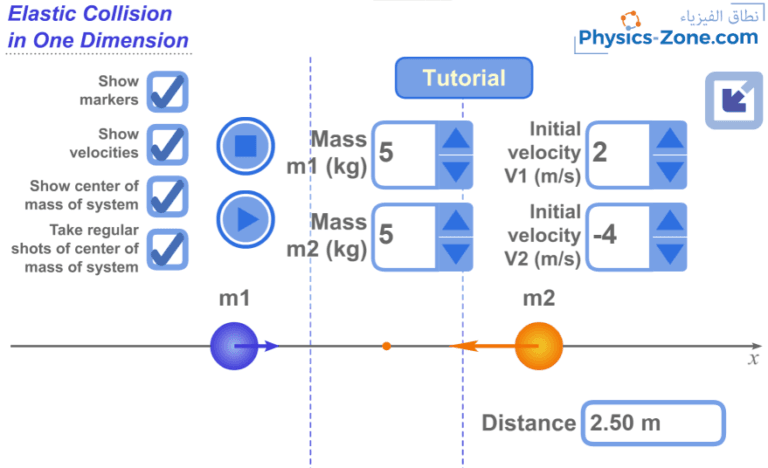
Inertia
لقراءة النسخة العربية أنقر هنا.
When you feel your body is leaning forward when the car is braking, or when your body leans backward when the car takes off, you are experiencing a property of your body that is called “inertia”. The greater the mass of your body, the more you feel this effect.
Inertia is defined as the resistance of the body to any change in its velocity. This includes changes to the body’s speed or direction of motion.